Protein Bars: The Perfect Fusion of Health and Taste
In the fast-paced world we live in, the perfect combination of health and taste is a goal pursued by many. To meet this demand, protein bars have emerged as a convenient, quick, and nutritionally rich snack. Today, we will delve into the details of this delicious and nutritionally abundant indulgence, taking you on a journey to discover the charm of protein bars.

The primary component of protein bars is protein, with common sources including whey protein, casein protein, soy protein, and others. Carbohydrates are also crucial components, derived from oats, fruits, whole grains, providing energy and enhancing texture. Additionally, the fat content in protein bars is generally low, often sourced from nuts and vegetable oils. Furthermore, protein bars may incorporate certain food additives such as sweeteners, thickeners, preservatives, enhancing the taste, stability, and shelf life of the bars.
To reduce the calorie and sugar content of protein bars, many use sugar substitutes to enhance sweetness, such as sorbitol, Isomaltitol, erythritol, and others. However, the taste of these sugar substitutes may not be suitable for everyone, and some individuals may even experience digestive discomfort after consumption.
The essential nutrients found in protein bars—such as proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, and minerals—contribute significantly to our overall health. They play a crucial role in supplementing protein intake, providing energy, managing weight, and boosting immune function. Additionally, protein bars come in a variety of enticing flavors, including chocolate nut, cocoa brownie, lemon, caramel macchiato, sea salt cheese, matcha dark chocolate, and butter cookie, catering to the diverse taste preferences of consumers.
The Global Protein Bar Market: Rapid Growth and Tremendous Potential
In an era focused on health, the popularity of protein bars is steadily rising due to an increasing number of people participating in fitness and sports activities. In recent years, the global protein bar market has shown a trend of rapid growth, with the market size expanding year by year, and is expected to continue this growth trajectory in the coming years. Among these, the Asia-Pacific region stands out as the fastest-growing area, witnessing significant success for various protein bar brands in this region [1]. With Asia's increasing influence on the protein bar market, the market potential and product innovation in countries like China are continually on the rise.
According to reports, the global protein bar market reached a size of $3.4 billion in 2022, and it is projected to reach $5.5 billion by 2028, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.35% between 2022 and 2028 [2]. As the world's second-largest economy, China's market size is expected to reach $1.7 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 9.6% during the analytical period from 2022 to 2030. Other notable regional markets include Japan and Canada, which are expected to grow by 3.2% and 4.9%, respectively, between 2022 and 2030. In Europe, Germany's estimated average compound growth rate is approximately 4.1%. With increasing demand for protein bars in various sectors such as sports nutrition and meal replacements, it is anticipated that the global protein bar market will reach $7.4 billion by 2030 [3].
Novel Food Ingredient – Yeast Protein
Protein's significance to the human body is self-evident, serving as a crucial component in the formation of human tissues and organs. To maintain bodily health, it is essential to ensure an adequate daily intake of protein. Currently, both per capita protein demand and global protein consumption are on the rise annually. With the increasing global population and insufficient supply of traditional proteins, a substantial "protein gap" is anticipated. Therefore, the development of sustainable alternative proteins or supplements proteins has become a hot research topic.

Yeast protein, derived from brewing yeast through a series of processes such as enzymatic hydrolysis and extraction, is a novel microbial protein with a protein content exceeding 80%. It holds promise as a new supplementary protein for food applications. As early as 1977, the U.S. FDA approved yeast protein from bread yeast as a protein nutritional supplement for use in food. In the same year, the EU also approved yeast protein obtained through conventional physical and enzymatic methods as a novel food. On December 1, 2023, yeast protein was included in the new food ingredient catalog by the National Health Commission of China.
Yeast protein is environmentally friendly and sustainable, featuring a short production cycle, low carbon emissions, and minimal need for extensive farmland, aligning with the principles of green development. Its production is stable, unaffected by seasons, climate, or genetic modification, making it suitable for industrial-scale production. Additionally, yeast protein boasts high nutritional value, with a comprehensive and balanced amino acid profile. Notably, lysine, the first limiting amino acid in cereal proteins, is also found in high levels in yeast protein. Its amino acid ratio is close to the ideal values recommended by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations [4]. A comparison of amino acid score (AAS) and digestible indispensable amino acid score (DIAAS) between yeast protein and animal proteins (whey protein concentrate, whey protein isolate) and plant proteins (wheat protein, pea protein) is presented in Tables 1 and 2. According to AAS, yeast protein surpasses plant proteins like soy protein and is comparable to whey protein. In terms of DIAAS, yeast protein slightly lower than whey protein and better than plant proteins.
Table 1: Amino Acid Score (AAS) for Different Proteins
FAO Model,mg/g, 2011 | AAS (>3 years old) | ||||||
Whey Protein Concentrate | Whey Protein Isolate | Soy Protein | Yeast Protein | Wheat Protein | Pea Protein | ||
Histidine | 16 | 150.2 | 161.9 | 202.2 | 204.3 | 160.6 | 164.2 |
Isoleucine | 30 | 218.3 | 241.6 | 169.2 | 224.4 | 130.9 | 160.6 |
Leucine | 61 | 181.5 | 191.3 | 131.9 | 161.7 | 112.5 | 126.6 |
Lysine | 48 | 168.2 | 166.6 | 99.5 | 156.7 | 31.6 | 128.8 |
Methionine + Cysteine | 23 | 220.1 | 224.2 | 110.5 | 136.7 | 74.0 | 73.0 |
Phenylalanine + Tyrosine | 41 | 211.1 | 242.9 | 271.7 | 300.8 | 268.3 | 243.9 |
Threonine | 25 | 305.2 | 289.4 | 170.8 | 228.6 | 123.7 | 159.9 |
Tryptophan | 6.6 | 309.2 | 269.4 | 216.9 | 228.6 | 138.0 | 134.8 |
Valine | 40 | 155.9 | 167.9 | 124.8 | 175.3 | 105.8 | 125.9 |
Table 2 Digestible Indispensable Amino Acid Score (DIAAS) of Different Proteins
FAO Model, 2011 | DIAAS (>3 years old) | |||||
Whey Protein Concentrate | Whey Protein Isolate | Soy Protein | Yeast Protein | Wheat Protein | Pea Protein | |
Histidine | 116.31 | 129.13 | 167.44 | 149.93 | 147.48 | 140.90 |
Isoleucine | 194.26 | 225.13 | 145.33 | 186.83 | 117.69 | 136.67 |
Leucine | 164.63 | 176.96 | 111.93 | 135.88 | 99.73 | 103.21 |
Lysine | 144.64 | 157.41 | 85.94 | 123.68 | 17.89 | 103.97 |
Methionine + Cysteine | 211.17 | 224.22 | 110.44 | 136.68 | 74.05 | 71.55 |
Phenylalanine + Tyrosine | 181.06 | 212.33 | 239.28 | 250.32 | 236.83 | 208.96 |
Threonine | 190.56 | 234.96 | 84.81 | 107.65 | 72.49 | 90.57 |
Tryptophan | 277.52 | 236.68 | 145.66 | 95.17 | 102.77 | 81.93 |
Valine | 133.59 | 153.51 | 103.03 | 144.58 | 91.76 | 98.99 |
Furthermore, yeast protein is a "slow" digesting protein with a high absorption rate, which prolongs the digestion time without affecting the utilization [5]. For an assessment of the digestive performance of yeast protein, refer to Figure 1. Simultaneously, Figures 2 and 3 illustrate the digestion rates of yeast protein and whey protein in gastric and pancreatic proteases, as well as the particle size distribution during in vitro digestion. From the figures, it is evident that the digestion rate of yeast protein is lower than that of whey protein. A lower digestibility of yeast protein concentrates is also attributed to the tighter microstructure and the higher level of β-sheets [6].
Figure 1. Percentage of non-digested protein from yeast protein, whey protein concentrate and soy protein isolate at different time.
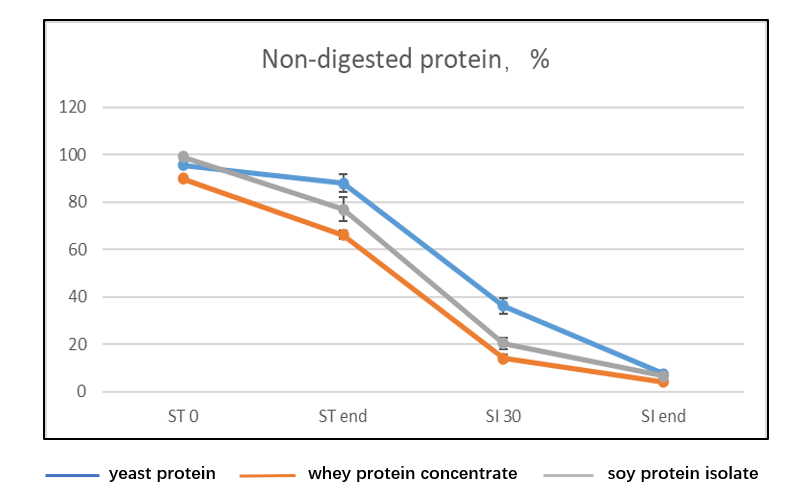
Figure 2. the digestibility of yeast protein (YP) and whey protein (WP) during pepsin and pancreatin digestion.
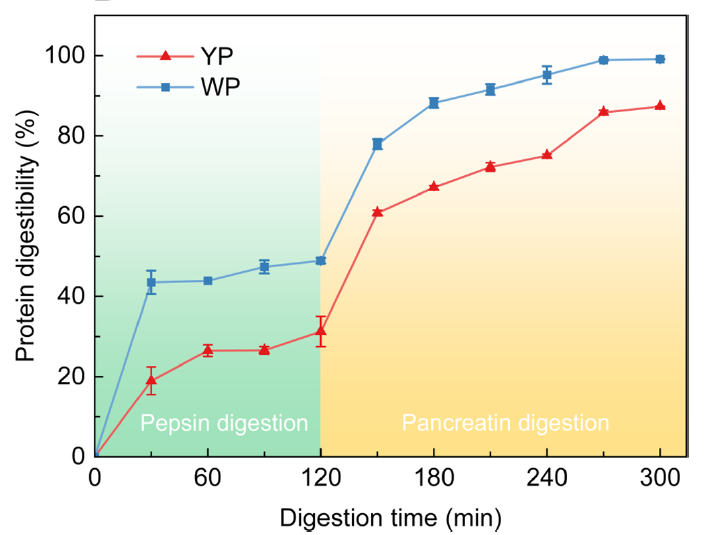
Figure 3. Particle size volume distribution of yeast protein (A), whey protein concentrated (B) and the sketch (C) during in vitro digestion.
Compared to traditional proteins, yeast protein is a novel protein source with various advantages, offering people a healthier and more sustainable dietary choice.
Application of Angel Yeast Protein in Protein Bars
In recent years, there has been a gradual global trend to expand from traditional crop and livestock resources to richer biological resources, to develop biotechnology and bio-industry, and to demand calories and protein from plant and animal microorganisms. Based on international trends and market changes, Angel conducted research on the application of yeast proteins in various industries, such as general foods (dairy products, protein drinks, plant-based meat, baked goods) and functional foods (protein powders, energy bars, protein bars) and functional foods (protein powder, energy bars, protein bars), etc.
Currently, in response to emerging consumer demands and consumption scenarios for protein bar products, Angel Yeast has developed multiple application solutions using yeast protein as a raw material. Among them, AngeoPro yeast protein F80 is one of the most widely used high-quality proteins developed by the company, with a protein content higher than 80%. It is rich in flavor and removes the soya flavor; there is no risk of genetic modification and no allergens are present, among other advantages. Introducing yeast protein into protein bars has multiple advantages as follows.
First, increased protein content. every 1% of added yeast protein can increase the protein content of protein bars by 0.8g, which provides fast and convenient protein supplementation for protein bar companies and improves the protein richness of protein bars. Secondly, nutrient enrichment. The addition of yeast protein makes the protein bar rich in various minerals, B vitamins, functional dietary fiber, and other nutrients, resulting in a more balanced nutritional profile. Additionally, the "slow" digestion and high absorption rate of yeast protein give the protein bar characteristics that alleviate hunger and extend the feeling of fullness, making it stand out among many protein bar products and serving as a major selling point. For those aiming to control weight and lose weight, this is undoubtedly an excellent choice. Thirdly, unique flavor. Yeast protein has a distinctive, subtle fermentation flavor with a pure taste. When combined with soy protein, whey protein, or other proteins in the preparation of protein bars, yeast protein can modify the beany flavors and other off-flavors, creating a more diverse and rich taste. Fourthly, ideal for vegetarians. For advocates of environmentalism or those who, due to religious beliefs, do not consume animal-derived foods, protein bars made primarily from yeast protein are an ideal choice. These protein bars do not contain animal-derived proteins, expanding the consumer base and meeting the needs of different populations. Fifthly, cost-effective. From a cost perspective, yeast protein is more cost-effective due to high production efficiency and lower costs compared to animal proteins like whey protein. If yeast protein is used in combination with or as a partial replacement for other proteins, such as animal proteins, it can significantly reduce the raw material costs of protein bars, leading to higher profits.
Using yeast protein F80 as raw material, Angel has successfully provided protein bar production customers with a variety of protein bar application Program. Among them, the two main products - the Lemon White Chocolate Flavored Protein Bar and the Nutty Dark Chocolate Flavored Protein Bar-not only have a rich taste but also contain three types of protein, with a protein content exceeding 30%. These two protein bars are sugar-free and gluten-free, with balanced nutrition, enhancing satiety, and supplementing energy. They have received unanimous praise from industry professionals at domestic and international exhibitions and can serve as high-quality meal replacement food.
As a new food for modern healthy snacks, protein bars are gaining popularity among consumers worldwide. Among the various protein sources for protein bars, yeast protein is emerging with its unique advantages and value, becoming a rising star in protein bar production. Choosing protein bars with yeast protein is choosing health and deliciousness. Let our lives be full of vitality, and let yeast protein accompany us towards a healthier and brighter future!
References:
[1] Protein Bar Market-Growth, Trends, and Forecasts (2023-2028), Mordor Intelligence, 2023. 4.
[2] Protein Bar Market: Global Industry Trends, Share, Size, Growth, Opportunity and Forecast 2023-2028, IMARC Group, 2023. 2.
[3] Protein Bars-Global Strategic Business Report-Product Image, Global Industry Analysts, Inc, 2023. 10.
[4] Ma J, Sun Y, Meng D, et al. Yeast proteins: The novel and sustainable alternative protein in food applications [J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 2023. 04. 003.
[5] Zhao YH, Zhang XW, Li K, Formation mechanism of yeast-soy protein extrudates during high-moisture extrusion and their digestive properties [J]. Food Hydrocolloids, 2023. 109093.
[6] Wang S, Huang F, Zhao Y, Slow-digestive yeast protein concentrate: An investigation of its in vitro digestibility and digestion behavior. Food Res Int. 2023, 174:113572.
About Angel Yeast
Founded in 1986, Angel Yeast Co., Ltd specializes in the production of yeast and yeast derivatives. Its product range includes baker's yeast and ingredients, Chinese dim sum and seasoning, savory yeast extract, human health, animal nutrition, plant nutrition, distilled spirits and biofuels, microbial nutrition and enzymes. At present, Angel Yeast has 11 international advanced production bases in China, Egypt and Russia, and provides products and services for more than 150 countries and regions globally.
About Angel Yeast Extract-Savoury:
Angel YE (yeast extract) made from edible yeast, by degradation the protein and nucleic acid in the yeast cells into nutritional seasonings with the application of modern biotechnology, has the advantages of increasing the fresh flavor, reducing salt, balancing the odor, strong tolerance and food properties, which promotes the global healthy operation of salt reduction and "clean label ".
Press Contact:
ANGEL YEAST CO.,LTD
Address: 168 Chengdong Avenue, Yichang, Hubei 443003, P. R. China
Tel: +86-717-6369520, 6369558
Fax: +86-717-6370680
Email: yefood@angelyeast. com




