Aquaculture faces challenges such as environmental pollution and disease epidemics, which require the search for effective feed additives. Glutathione (GSH), a tripeptide containing sulfhydryl groups, has functions such as antioxidant, detoxification and immune enhancement. This paper reviews the research progress of glutathione in aquaculture.
1. The source and synthesis method of glutathione
Glutathione is a tripeptide composed of three amino acids (glutamate, cysteine, and glycine), which are widely distributed in nature in animals, plants, and microorganisms. In animals, glutathione is synthesized mainly by two pathways: (1) protein containing glutathione or its precursors (such as cysteine) is ingested from food and absorbed after being hydrolyzed in the digestive tract; (2) it is synthesized directly from the three amino acids in cells catalyzed by two key enzymes (γ-glutamylcysteine synthase and glutathione synthase)
Glutathione is available in both reduced (GSH) and oxidized (GSSG) forms, with the reduced form predominating in the majority of cells. Reduced glutathione is a single molecule in which the active sulfhydryl group (-SH) on the cysteine confers a variety of important functions. Oxidized glutathione, on the other hand, is a dimer of two reduced molecules bound together at the sulfhydryl group and is more present only under extracellular or stress conditions.
Glutathione can be produced by chemical synthesis methods, enzyme conversion methods, and fermentation methods. Among them, the fermentation method is the most commonly used and environmentally friendly method, which uses microorganisms (such as yeast) to accumulate a high concentration of GSH during the fermentation process using cheap raw materials (such as glucose or honey) and then obtains high purity and pollution-free GSH products through isolation and purification.
2. Application of glutathione in aquatic
During aquaculture, stress factors can lead to metabolic disorders, decreased disease resistance, and disease outbreaks in aquatic animals. Free radicals cause damage to cell membranes and nucleic acids, thereby disrupting the antioxidant defense system of aquatic animals. In addition to environmental changes, excessive oxidation of fats and oils in feeds can also affect the antioxidant defense system of aquatic animals. Relevant literature reports that glutathione has good applications in dealing with these stress responses and metabolic imbalances.
2.1. Effects of glutathione on the growth of aquatic animals
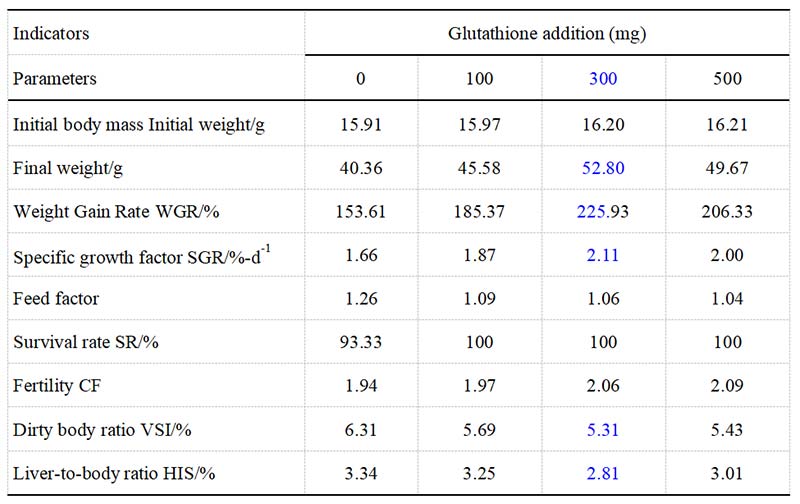
Glutathione, as an endogenous growth regulator, can promote the growth and development of aquaculture animals by affecting the endocrine system, protein synthesis and catabolism, and energy metabolism. For the study of California perch, it was found that the weight gain rate and specific growth coefficient of the experimental group were significantly higher than those of the control group when 0, 100, 300 and 500 mg/kg of glutathione were added to the diet, and the best at the addition level of 300 mg/kg.
Table 1: Each microbial culture method and detection site
2.2 Effects of glutathione on the liver and intestinal tract
The main effects of glutathione on the liver and intestine of aquatic animals are as follows:
(1) Reduction of oxidative stress: In the liver of aquatic animals, glutathione can reduce the level of oxidative stress by scavenging free radicals and toxic substances. This helps maintain the health of liver cells and protects the liver from damage caused by pathogenic microorganisms, environmental pollutants, and other harmful substances.
(2) Promotion of detoxification metabolism: Glutathione can also promote the process of liver detoxification metabolism and participate in the conversion and excretion of toxic substances in the body. This helps to reduce the sensitivity of aquatic animals to toxic substances and protect the health of the liver.
(3) Maintenance of protein synthesis: Glutathione can participate in protein synthesis in the liver and maintain the normal growth and metabolism of liver cells. This helps to maintain the stability and health of liver function.
(4) Maintenance of the integrity of the intestinal mucosa: In the intestine of aquatic animals, glutathione can maintain the integrity of the intestinal mucosa and prevent harmful substances and microorganisms from entering the bloodstream. This helps to protect the health of aquatic animals and reduce the occurrence of diseases.
(5) Promotion of the growth of beneficial bacteria: Glutathione can promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in the intestine and maintain the balance of intestinal flora. This helps to improve the immunity and digestive ability of aquatic animals and reduce the incidence of diseases.
Figure 1 Comparison of liver and intestine of different groups of California perch
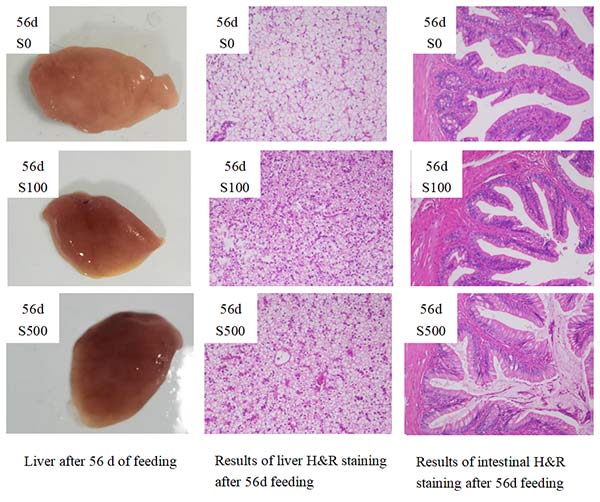
In Figure 1, compared with the control group, the liver of California perch was significantly more bright red in color, and the fat deposition in the liver was also significantly lower compared with the control group, and the thickness and width of intestinal villi were significantly increased, indicating that glutathione could significantly improve the digestive health and growth performance of California perch.
2.3 Effect of glutathione on detoxification and antioxidant capacity of aquatic animals
Glutathione has a variety of physiological functions, in addition to its effect on the growth and development of aquaculture animals, it is also an antioxidant and detoxifier. As an antioxidant, glutathione can scavenge reactive oxygen radicals in the body, protect cells from oxidative damage, and improve the antioxidant capacity of animals. The mechanism of action of glutathione is comprehensive, including direct blocking of chain reaction and synergistic action with other antioxidants to form a dynamic antioxidant system.
Five groups of different levels of glutathione were added to the diet of Pelteobagrus fulvidraco at 0, 100, 300, 500 and 700 mg/kg net, respectively, and the experiment showed that glutathione significantly improved the antioxidant capacity of liver of Pelteobagrus fulvidraco.
Figure 2 Effect of GSH addition on the main antioxidant indexes of liver in Pelteobagrus fulvidraco feed
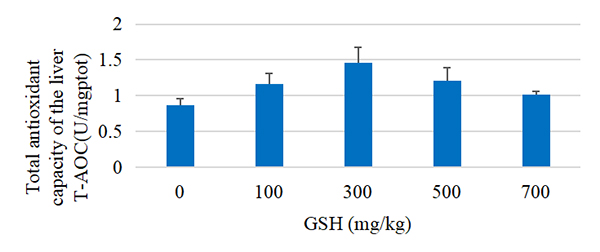
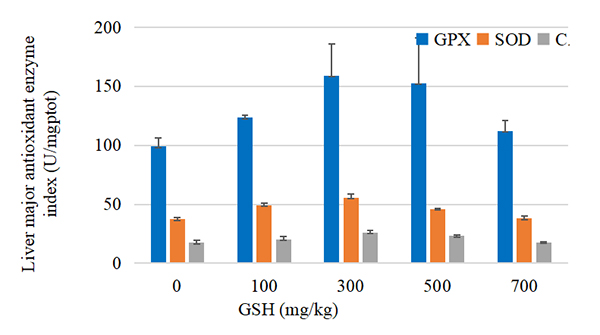
Note: T-AOC is total antioxidant capacity, GPX is glutathione peroxidase, SOD is superoxide dismutase; CAT is catalase
In addition, glutathione also has detoxification function. Relevant research shows that glutathione can remove toxic substances such as microcystins, aflatoxins, heavy metals and peroxides, and can combine with these toxic substances in aquatic animals so that their toxicity can be significantly reduced, thus protecting the organism to reduce the damage of toxins.
3. Prospects of glutathione in aquaculture
The use of glutathione in aquaculture shows great promise, but there are certain trends and issues that need to be addressed. Establishing quality standards and a regulatory system, developing multiple application forms, and strengthening scientific research and application promotion are key to the further development of glutathione in aquaculture. It is imperative that all stakeholders work collaboratively to enhance research efforts and promote the application of glutathione, in order to foster continued progress and improvement in this field.
 | Published by An Fenghe Engineer of Animal Nutrition Division |
About Angel Animal Nutrition:
Fubon is a brand of Angel Animal Nutrition. Fubon is committed to developing natural, efficient microbial feed derived from yeast with Angel's leading technology in yeast industry, providing the best service solutions for the nutrition and health in animals. Angel Animal Nutrition creates value for global feed and animal agriculture customers through continuously upgraded products and professional services.
About Angel:
Angel Yeast Company is a high-tech listed company specializing in yeast and biotech. Product business covers Yeast and Baking, Yeast Extract-Savoury, Nutrition & Health and Biotechnology fields. It is one of the world's leading companies in the yeast industry. Angel has 12 holding subsidiaries and provides products and services for more than 150 countries and regions.
Press Contact:
ANGEL YEAST CO.,LTD
Address: 168 Chengdong Avenue, Yichang, Hubei 443003, P. R.China
Tel:+86-717-6369520, 6369558
Fax:+86-717-6370680
Email: aie@angelyeast.com







