By Zheng Zhong
Escherichia coli expression system is the most widely used one in protein, and about 30 percent of recombinant protein products are produced by the system. A large number of organic nitrogen sources, such as yeast extract and peptone, will be used in the cultivation of E. coli, however, the traditional animal peptone has risks of safety and regulatory such as pathogenic factors and custom taboos, and de-animalization source is an inevitable trend. Whether plant-derived peptone will affect the bacteria density and protein expression of E. coli after replacing animal peptone will have direct bearing on the production benefit and is also an important indicator for enterprises to select raw materials.
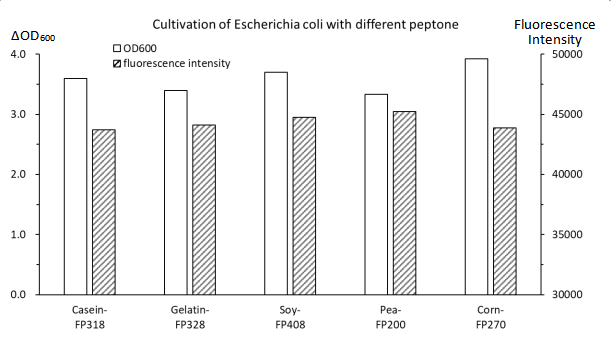
From the results of the above figure, it can be found that the expression levels of OD600 and green fluorescent protein are different when E. coli is cultured with different peptone. Among them, the biomass and expression level of E. coli with soybean peptone FP408 as the nitrogen source both exceed that of animal peptone (casein peptone FP318 and gel peptone FP328). Although pea peptone has a slightly lower biomass than that of other peptone, it achieves the highest expression level, with per unit bacteria reaching 13577, which is 11.7 percent higher than that of casein peptone. At the same time, although the expression level of corn peptone was relatively low, its biomass was higher than that of other peptone.
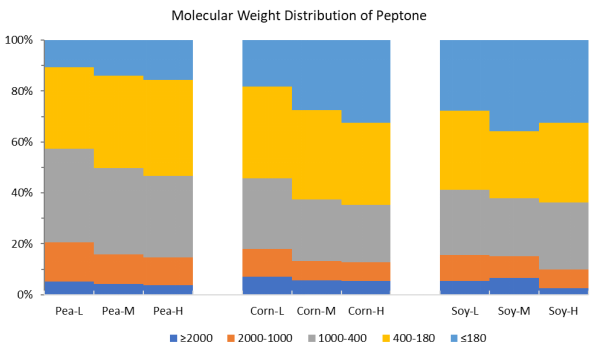
As shown in the figure above, pea, corn and soybean peptone with different degrees of hydrolysis (L, M and H represent low, medium and high degrees of hydrolysis respectively) are obtained through the control of enzymatic hydrolysis. The peptone with its molecular weight distribution showing high hydrolysis degree is more abundant in the small molecular weight peptide fragment. With the use of the above peptone products to culture E. coli, the test results are shown in the following figure:
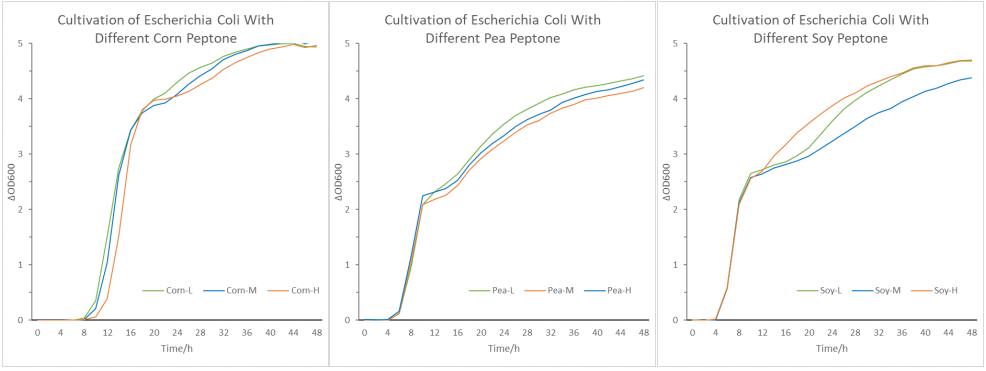
From the results above, it can be found that the growth of E. coli is different with different hydrolysis degrees of the same peptone. Corn peptone and pea peptone with low hydrolysis degree are more conducive to the rapid growth of E. coli, but their final extreme values are close. On the contrary, soybean peptone with high degree of hydrolysis is more benefit for the growth of E. coli, and its growth curve is smoother, indicating that E. coli can maintain a long period of vigorous growth.
According to the relevant content of this study, it can be found that different plant peptones have different advantages and effects on the growth and expression of E. coli. Among them, the soybean peptone FP408 has reached the same level of animal peptone in terms of the biomass and expression level of E. coli, providing a new choice for the industrial production of recombinant protein of E. coli system. At the same time, the comparison of different models of similar products shows that pea peptone and corn peptone are relatively stable, while soybean peptone has high plasticity. When selecting soybean peptone from different sources, it is necessary to compare various models before making judgment.
 | Published by Zheng Zhong R&D expert of Protein Nutrition and Flavoring technology center |
About Angel Microbial Nutrition:
About Angel: