By Wang Chao
What's the difference between autolyzed Yeast and inactivated yeast?
Inactivated yeast, which has complete yeast cells, and there is a product that is close to inactivated yeast, which we called autolyzed yeast powder. Living yeast has relatively abundant autolyzing enzymes. These enzymes can be activated under certain conditions and can degrade their protein, nucleic acid, and other components to a certain extent. People use this mechanism to make yeast products that are Yeast autolyzed powder.
Characteristics of Angel autolyzed Yeast
> Due to the yeast autolyzed powder, nutrients such as protein and nucleic acid are degraded to a certain extent, and the cells are also damaged to a certain extent. Therefore, compared with inactivated yeast, microorganisms will absorb and utilize faster, perform faster, and better promote the growth of bacteria. However, compared with yeast extract, the degradation of nutrients is not sufficient, and the delayed effect is more than that of the performance.
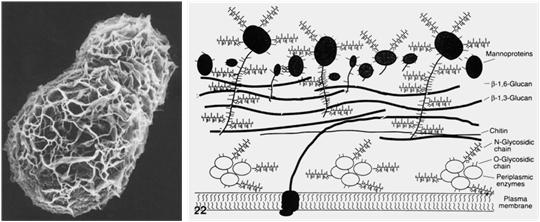
> The complete cell structure can be observed under the microscope of yeast autolyzed powder, but the cell wall is damaged to a certain extent. Because of the cell wall, the cell wall is made of high molecular polymer, so the water is poorly water-soluble, and the solution is turbid. Users who have higher requirements for the clarity of organic nitrogen sources are restricted from use. Although the cell wall is macromolecular and inert, it binds a large number of macromolecular proteins with the cell wall and cell membrane. The cell membrane is rich in phospholipid bilayers and also contains nutritional components such as ergosterol, which also gives yeast self-dissolving powder. Special nutritional characteristics.
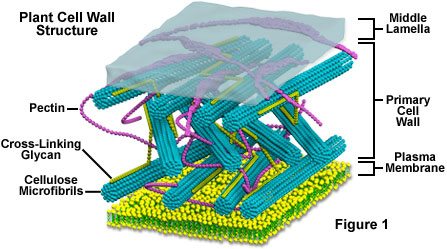
> Compared with yeast extract, yeast autolyzed powder has no cell wall separation process. During the separation process, there must be a reduction in nutrients. Yeast autolyzing powder has no cell wall separation, which can more completely retain the nutrition of yeast.
Functions of Yeast autolyzed powder:
> Promote the growth of bacteria and increase the number of bacteria, and can be used in the fermentation industry that is more cost-sensitive;
> Rich in macromolecular proteins, it enhances the continuity of fermentation of bacteria and actinomycetes, and promotes the accumulation of metabolites.
About Angel: