By Yu Kui
Some biochemical drugs are typically synthesized by traditional chemical methods. In recent years, research has found that yeast cell enzymes are abundant and efficient cellular catalytic factories, capable of enzyme-catalyzed synthesis of certain substances. Compared with chemical methods, enzyme methods have the advantages of mild reaction conditions, higher reaction rates, and greater environmental friendliness, and are increasingly favored by researchers. This article reviews the enzyme-catalyzed synthesis of some common drugs such as NTP, FDP, phosphatidylcholine, and 2-phenylethanol using active dry yeast.

1. Catalyzing the Synthesis of NTP Using Yeast Cells
Nucleoside-5’-triphosphates (NTPs) include cytidine-5’-triphosphates (CTP), adenosine-5’-triphosphates (ATP), guanosine-5’-triphosphates (GTP), and uridine-5’-triphosphates (UTP). NTPs play important roles in biological cells, serving not only as important precursors for ribonucleic acid synthesis but also as essential energy molecules involved in energy transfer, storage, phosphorylation, and other metabolic processes in the body.
There are many pathways for the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and currently, using active dry yeast as an enzyme source to catalyze the biological synthesis of ATP from adenosine monophosphate (AMP) is one of the most promising methods in industry. It is reported that replacing AMP with adenosine (AR) as a reaction substrate can also achieve the conversion of ATP while reducing substrate inhibition and production costs. Coupling the energy metabolism process of active dry yeast with adenosine as a substrate can achieve the biological transformation of adenosine to ATP, and the reaction mechanism is shown roughly in Figure 1, which requires the participation of multiple enzymes.

CTP, GTP, and UTP are synthesized like ATP, and the use of biocatalysts to synthesize nucleotides is becoming increasingly widespread, replacing traditional methods. Currently, some companies have already achieved the production of NTP using active dry yeast instead of brewer's yeast.
2. Synthesis of FDP Using Yeast Cell Biocatalysis
Fructose-1,6-diphosphate (FDP) has a molecular formula of C6H14O12P2 and a molecular weight of 340.1. It is commonly found in the form of salts such as sodium, calcium, and zinc. FDP has functions such as increasing intracellular high-energy phosphate concentration, promoting potassium ionreflux, restoring cell polarization, increasing cell utilization of glucose, repairing cell damage, etc. It is an intermediate of glycolysis and has the efficacy of regulating several enzymes of glucose metabolism. FDP is a biochemical drug that restores and improves cellular metabolic molecular levels, mainly used in cardiovascular adaptation. Additionally, FDP also has applications in the production of health foods and cosmetics.
There are various methods for synthesizing FDP. Due to the low cost and convenient source of waste beer yeast, the main method is catalyzed by yeast enzymes using glucose or sucrose and inorganic phosphate as raw materials. Typically, the Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas pathway of yeast glycolysis is used. By changing the cell membrane permeability and controlling the cell enzyme system, such as blocking aldolase, FDP is synthesized and released into the fermentation solution. The specific process involves breaking down the washed waste yeast or active dry yeast by chemical methods to release active enzymes, mixing the yeast solution with a reaction solution containing sugars and phosphate, carrying out a biological synthesis reaction to produce FDP, and then purifying, concentrating, decolorizing, crystallizing and further purifying the reaction solution to obtain pure FDP. Currently, there are still problems with low conversion rate and extraction rate, high production cost, and organic solvent pollution in the production process of FDP.
Active dry yeast has the advantages of high enzymatic activity, easy wall-breaking, and good stability. The use of active dry yeast instead of waste beer yeast is one of the future trends.
3. The Biocatalytic Synthesis of Phosphatidylcholine Using Yeast Cells.
Sodium phosphatidylcholine is a drug with definite therapeutic effects and wide clinical applications. It has a certain role in promoting the recovery and awakening of brain function and is mainly used to treat functional and consciousness disorders caused by acute damage to the central nervous system.
There are many methods for preparing phosphatidylcholine, which can be roughly divided into three pathways. One is organic chemical synthesis, which has problems such as difficulty in separating the product from the condensing agent, unsuitability for medicinal use, low reaction conversion rate, many by-products, high cost, and serious environmental pollution. The second is microbial fermentation, which has problems such as low product concentration and unstable yield. The third is enzymatic synthesis, such as using active dry yeast for biocatalysis, which has the advantages of simple process, high conversion rate, and low cost. China has developed the technology of catalytic synthesis of phosphatidylcholine using yeast cells since the 1970s, and the process flow chart is shown below:
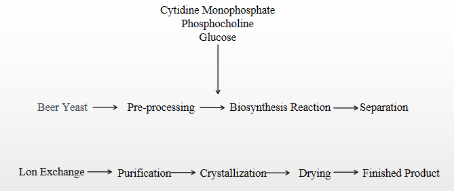
Under the catalysis of beer yeast or active dry yeast, phosphatidylcholine sodium is synthesized using cytidine monophosphate, phosphocholine, glucose, and inorganic salts as starting substrates. Due to the unstable supply and low enzyme activity of beer yeast, it is an inevitable choice to replace beer yeast with active dry yeast.
4. Biocatalytic Synthesis of 2-Phenylethanol Using Yeast Cells
2-Phenylethanol is an aromatic alcohol with a soft and delicate rose-like fragrance. Many plants in nature have a pleasant aroma because of their 2-phenylethanol content, such as roses, jasmine, yellow orchids, and lilies. The fragrance of 2-phenylethanol is highly popular and is a mainstream style in the international flavor and fragrance industry. Currently, 2-phenylethanol is mainly produced by the benzene-epoxide synthesis method or the hydrogenation of styrene oxidation method, which have drawbacks such as high toxicity of raw materials, low product purity, and significant pollution in the synthesis process.
Yeast cells can synthesize 2-phenylethanol themselves. In production, yeast cells for brewing can be first cultured, and then L-phenylalanine is added as a substrate, along with nutrients such as sucrose and ammonium sulfate. The process is catalyzed by yeast for about 40 hours to complete the production.
5. The Application of baker's yeast in Asymmetric Reduction
Baker's yeast contains abundant oxidoreductases that can catalyze the asymmetric reduction of various carbonyl compounds. Using whole-cell catalysis with baker's yeast, the addition of inexpensive carbon sources can regenerate expensive coenzymes, greatly reducing production costs.
Yang Zhonghua added allyl compounds to baker's yeast and Ma Xiaokui added β-cyclodextrin as chiral catalyst to achieve asymmetric reduction of carbonyl compounds. On the basis of synthesizing β-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid ice ester, Kuang Xinmou used baker's yeast to asymmetrically reduce and synthesize tanshinone ice ester (DBZ).

6. Bottom line
With the development of biotechnology, yeast cell catalysis has become a cutting-edge technology that attracts much attention in the field of drug synthesis. In this context, YA200, the active yeast powder developed by ANGEL YEAST can provide a more efficient and environmentally friendly solution for drug preparation.
As an efficient catalyst, active yeast powder has a wide range of applications in the field of drug synthesis. Firstly, the use of yeast cell catalysis to synthesize NTP can effectively improve the efficiency and yield of drug production. In addition, active yeast powder has also demonstrated good potential for application in the biological catalytic synthesis of FDP, phosphatidylcholine, 2-phenylethanol, and other compounds. Bread yeast also provides a more convenient solution for the preparation of chiral compounds in asymmetric reduction.
Compared with traditional chemical synthesis, yeast cell catalytic synthesis has advantages such as mild reaction conditions, higher reaction rates, and environmental friendliness. Moreover, YA200 active yeast powder not only has high yeast cell activity and stability, but can also be customized according to customers' different needs, providing tailor-made solutions for drug synthesis. In addition, YA200 active yeast powder can not only be applied in the field of drug preparation, but also in the preparation process of other biological products, such as food and cosmetics. In these fields, yeast cell catalytic synthesis also has a wide range of applications.
In summary, YA200 active yeast powder will provide a more efficient and environmentally friendly solution for drug preparation and the preparation of other biological products.
About Angel Fermentation Nutrients:
About Angel: